The impact of data breaches, industry-specific security policies for data protection, and how a multi-layered approach to cloud security holds the key.
As individuals, we go through life sharing information about ourselves in every aspect of our daily existence. From credit checks for securing a loan, through to entire personal and family medical histories for securing health insurance. Without providing personal data, many services would be unavailable to the average person – but in our modern online world, we are more cognizant than ever about where our data is going, is the data secure, who has access, and whether it will be shared with third parties.
Once we relinquish our personal information to legitimate organizations, they become the ‘data processor’, and their data security focus will be governed by industry-specific standards. Individuals can certainly be encouraged to play their part, for example, blocking suspicious contacts, installing antivirus software on a personal computer or using biometric security. But for genuine transactions, the responsibility for protecting our personal data must lie with the custodians.
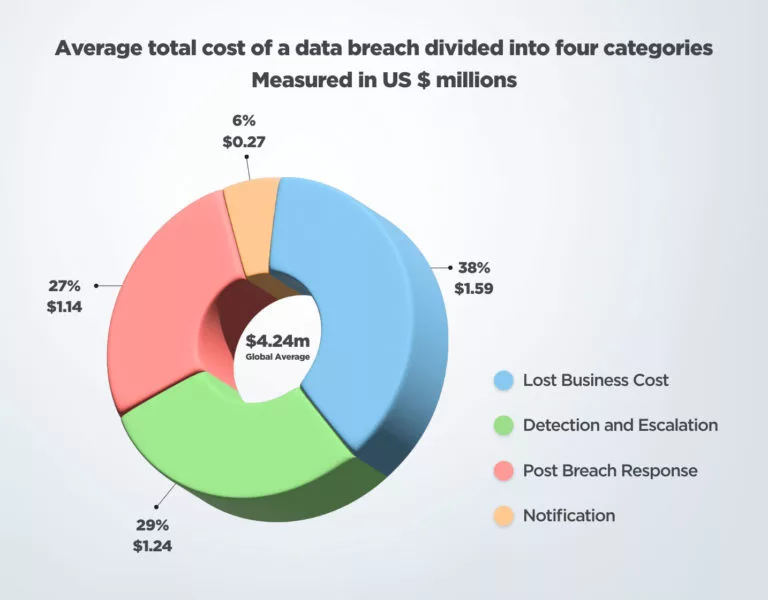
Unfortunately, hackers find ever more creative ways to breach firewalls, and scammers continue to prey on the vulnerable, or those momentarily caught ‘off-guard’, in order to gain access to the most valuable information. And the cost of a data breach can be devastating:
Industry-Specific Data Security Compliance
In the US, no single data privacy legislation exists, with data protection laws being a combination of both federal and state-level statutes to address specific sectors. The good news is that in May 2021, the US President signed an Executive Order on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity, to help strengthen data protection and modernize cybersecurity defenses.
Naturally, certain industries, just by the very nature of their business and the type of data they handle, will already be security and compliance-centric, adhering to robust data security compliance regulations. Industry examples include:
- Healthcare and Life Sciences: an industry that processes and handles possibly the most sensitive and confidential personal information. It is focused on the ability to safely and securely integrate applications used by care providers, insurance providers, patients and their caregivers. In addition, data security is key when you consider that medical records retention policies in some states require storage for up to 30 years.
- Regulations include: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), HIPAA Security Rule, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR, applies to US organizations that store or process personal data of EU residents)
- Finance: an industry that is entirely reliant on digital platforms, and therefore, a prime target for cybercriminals. It is focused on protecting customer assets, as well as personally identifiable information (PII), from malicious activity, especially as online transactions now dominate the finance market.
- Regulations include: Gramm Leach Bliley Act (GLBA), Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS)
- Telecommunications: this is an industry where organizations are expected to be highly tech-savvy, with global interconnectivity and digital infrastructures being at the heart of its operations. The core focus is protecting network highways and communication systems, while at the same time protecting large volumes of PII, as a result of its subscription-based format.
- Regulations include: Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA), Computer Fraud and Abuse Act, Electronic Communications Privacy Act
- Insurance Sector: with a unique combination of financial and personally identifiable data, including medical IDs and social security numbers, the insurance sector is an obvious target for fraudsters. Data security, and maintaining customer trust and loyalty, is paramount to an insurance organization’s survival.
- Regulations include: NAIC Insurance Data Security Model Law, NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation, as well as GLBA, HIPAA
How Cloud Holds the Key
The recent ISC2 2020 Cloud Security Report found that 34% cybersecurity professionals say the risk of data security, loss or leakage deters cloud adoption in their organization. Addressing the question of “Will my data be safe on the cloud?”, 62% of respondents invested in cloud native security technology, alongside employee certification, to keep pace with ever-evolving security demands.
With the big data explosion, migrating to the cloud – public, private, or hybrid – is almost an inevitability. With more data predicted to be generated in the next three years than in the whole of the last three decades put together, cloud technology will be all-pervading. Therefore, as organizations recognize cloud tech benefits for scalability, increased agility, and reduced TCO, the ability to put your trust in cloud security is also crucial.
In the same ISC2 report, 78% respondents believe they or their teams are not equipped to operate in cloud environments. And this where reputable cloud providers, with the requisite skills and expertise, can address cloud data security concerns:
- Deep Technical Know-HowEven when enterprises have well-established internal IT resources, these departments are managing many aspects of the business but not necessarily experts in cloud cybersecurity. Leading cloud providers develop large teams of highly qualified professionals, whose sole focus is that of protecting data in the cloud. They are at the forefront of dynamic and rapidly advancing cloud security tools and services, can recommend and implement tougher security measures, and provide an unmatched level of expertise.
- Risk Mitigation StrategiesA cloud provider will not only incorporate the very latest in cloud security technology but also leverage game-changing automation and AI. The ability to detect threats before a breach occurs, and automatically initiate next steps for troubleshooting, brings the highest level of security.
- Industry Regulation ComplianceWhen new industry regulations are issued, or existing ones updated, you need the confidence to know that your systems comply. Cloud providers with relevant industry compliance certification can ensure clients’ systems always meet strict data security standards, for example, AWS Healthcare Competency Partners.
- Real-Time MonitoringIncorporating sophisticated cloud data and analytics services will deliver reporting and audit functionality. Business insights into potential vulnerabilities are identified and prioritized, helping to create the most effective, resilient, and secure infrastructures.
Bottom Line: Data security in the cloud is achieved with a multi-layered approach. Cloud providers implement the most advanced cloud security services, freeing up CTOs and CIOs to focus on improving internal data security awareness, training, and data access policies. This collaborative approach towards maximizing data security helps to break down the barrier to cloud adoption and build trust in the powerful cloud security technology available today.
Discover how SourceFuse provides the reassurance of compliant cloud data security services, allowing you to focus on your core business innovation.